Regenerative Agriculture: Using Precision Ag Tools To Work with Nature, for Nature

In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of regenerative agriculture practices and the role of precision ag tools and technologies in supporting these practices. We will also discuss some of the challenges and limitations of using these tools and highlight successful examples of their implementation.

Going beyond sustainability
As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change and the growing demand for food, the need for sustainable agriculture practices has never been more pressing. However, while sustainability is a critical goal for agriculture, it may not be enough to address the environmental and social challenges we face today. Sustainability aims to maintain current levels of resource use and ecosystem services, but it does not necessarily address the need for restoration and regeneration of degraded ecosystems.
Regenerative agriculture, on the other hand, goes beyond sustainability and aims to restore and enhance the health of soil, water, and ecosystems while also supporting healthy food systems and local communities. Regenerative agriculture practices emphasise the importance of building healthy soils that support the growth of diverse crops and the conservation of biodiversity. By focusing on regenerative agriculture practices, we can improve the resilience of our agricultural systems to climate change, increase carbon sequestration in the soil, and reduce the use of harmful chemicals and synthetic fertilisers.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the main principles that govern regenerative land management:
- Minimising soil disturbance: Tilling and other forms of soil disturbance can disrupt the soil structure and deplete organic matter. Regenerative agriculture practices, such as no-till or reduced-till, minimise soil disturbance to maintain soil health.
- Maximising soil cover: Cover crops, crop rotations, and intercropping are examples of practices that increase the amount of vegetation on the soil surface, which helps to protect the soil from erosion, retain moisture, and build organic matter.
- Diversifying crops and livestock: Growing a variety of crops and raising multiple species of livestock can increase biodiversity, reduce the risk of pests and diseases, and improve soil health.
- Integrating livestock and crops: Grazing livestock on cover crops or crop residue can improve soil health by cycling nutrients and breaking down organic matter. Livestock also contribute to soil health through their manure.
- Using natural inputs: Regenerative agriculture relies on natural inputs such as compost, animal manure, and biostimulants to supply nutrients to the soil and support plant growth.
- Managing pests and diseases with ecological approaches: Regenerative agriculture utilises ecological approaches to manage pests and diseases, such as crop rotation, biological control, and the use of natural predators.

The power of regenerative farming
Regenerative farming has the power to transform our agricultural systems from a source of environmental degradation to a force for building healthy soils, promoting biodiversity, and mitigating climate change.
The benefits of regenerative agriculture are numerous and include improved soil health, increased biodiversity, climate change mitigation, reduced water usage, improved animal welfare, and resilience to extreme weather events. Let’s take a closer look at each of these:
- Improved soil health: Regenerative agriculture practices can improve soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, and increasing soil fertility. This can lead to increased crop yields, reduced erosion, and improved water retention.
- Increased biodiversity: Regenerative agriculture practices can increase biodiversity by providing habitat for beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. This can help to reduce the need for synthetic inputs such as pesticides and herbicides.
- Climate change mitigation: Regenerative agriculture can help to mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil. Healthy soils can store large amounts of carbon, reducing the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
- Reduced water usage: Regenerative agriculture practices can improve water retention in the soil, reducing the amount of irrigation needed. This can lead to reduced water usage and improved water quality.
- Resilience to extreme weather: Regenerative agriculture practices can improve the resilience of the land to extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. Healthy soils can retain more water, reducing the impact of droughts, while improved soil structure can reduce erosion and prevent flooding.
- Improved animal welfare: Regenerative agriculture can improve animal welfare by providing animals with access to natural habitats and reducing the use of antibiotics and other synthetic inputs.
Using precision agriculture to work with nature, for nature
Precision agriculture plays a key role in implementing and maintaining regenerative agriculture practices. By monitoring and managing soil health, promoting biodiversity, and reducing the use of harmful chemicals and synthetic fertilisers, precision agriculture can help farmers to work with nature, for nature, and create sustainable and resilient agricultural systems that support healthy ecosystems and communities.

Improved Soil Health

Increased Biodiversity

Reduced Chemical Use
Improved soil health
Healthy soil is the foundation of a healthy ecosystem and can improve crop productivity, water retention, carbon sequestration, and nutrient cycling. One of the primary ways that precision agriculture can be used in regenerative agriculture is to monitor and manage soil health.
Smart farming tools such as soil sensors can provide growers with real-time information on soil moisture, nutrient levels, and other critical parameters. By monitoring soil health and adjusting soil management practices accordingly, growers can build healthy soils that support the growth of diverse crops and the conservation of biodiversity.
Increased biodiversity
Another way that smart farming technology can be used in regenerative agriculture is to promote biodiversity. Biodiversity is critical for ecosystem health, and regenerative agriculture aims to promote the growth of diverse crops and the conservation of natural habitats.
Remote sensing technology help growers monitor and manage crop growth and identify areas where habitat conservation is needed. Precision agriculture can also help farmers to implement better cover cropping and reduced tillage practices, which can improve soil organic matter, reduce erosion, and increase soil fertility, promoting biodiversity in the process.
Reduced use of harmful chemicals
Precision agriculture can also help farmers to reduce the use of harmful chemicals and synthetic fertilisers, leading to healthier ecosystems and a reduced environmental impact. By using the available technologies to monitor crop growth and pest infestations, growers can adopt a more proactive method of managing pests and diseases. By acting early to threats, and using chemicals only where and when absolutely necessary, chemical use can be drastically reduced leading to an overall healthier environment.

Precision ag tools and technologies that are changing the game
Agriculture has come a long way from its traditional roots. The digital revolution has opened up a world of sustainability opportunities for the farming industry. To achieve regenerative agriculture goals, farmers and their teams must use various tools and technologies to help them monitor and manage soil health, promote biodiversity, and reduce environmental impacts.
Some of the key tools and technologies that are changing the game in regenerative agriculture include soil moisture sensors, remote sensing technologies and farming data platforms. By leveraging these tools, regenerative farmers can create more sustainable and resilient farming systems that benefit both the environment and the growers themselves. Let’s take a look at each for these in more detail:
Soil moisture sensors
Soil moisture sensors are one of the most important tools for monitoring soil health in regenerative agriculture. These sensors allow farmers to measure soil moisture levels in real-time, helping them to make more informed decisions about irrigation and fertilisation. By using soil moisture sensors, farmers can reduce water waste, improve crop yields, and promote healthy soil that supports biodiversity.
Remote sensing technology
Remote sensing is another technology that is changing the game in regenerative agriculture. Remote sensing technologies, such as drones and satellites, can provide farmers with high-resolution imagery of their crops and fields. This imagery can be used to identify areas of stress, track crop growth, and monitor soil health. By using remote sensing technologies, farmers can make more informed decisions about crop management, reducing environmental impacts and promoting healthy soil.
Farming data platforms
Farming data platforms are also changing the game in regenerative agriculture. These platforms allow farmers to collect, store, and analyse data from a wide range of sources, including soil moisture sensors, remote sensing technologies, and weather stations. By using farming data platforms, farmers can make more informed decisions about crop management, reducing waste, and increasing yields. These platforms can also help farmers to collaborate with other farmers and share best practices, promoting the growth of regenerative agriculture around the world.
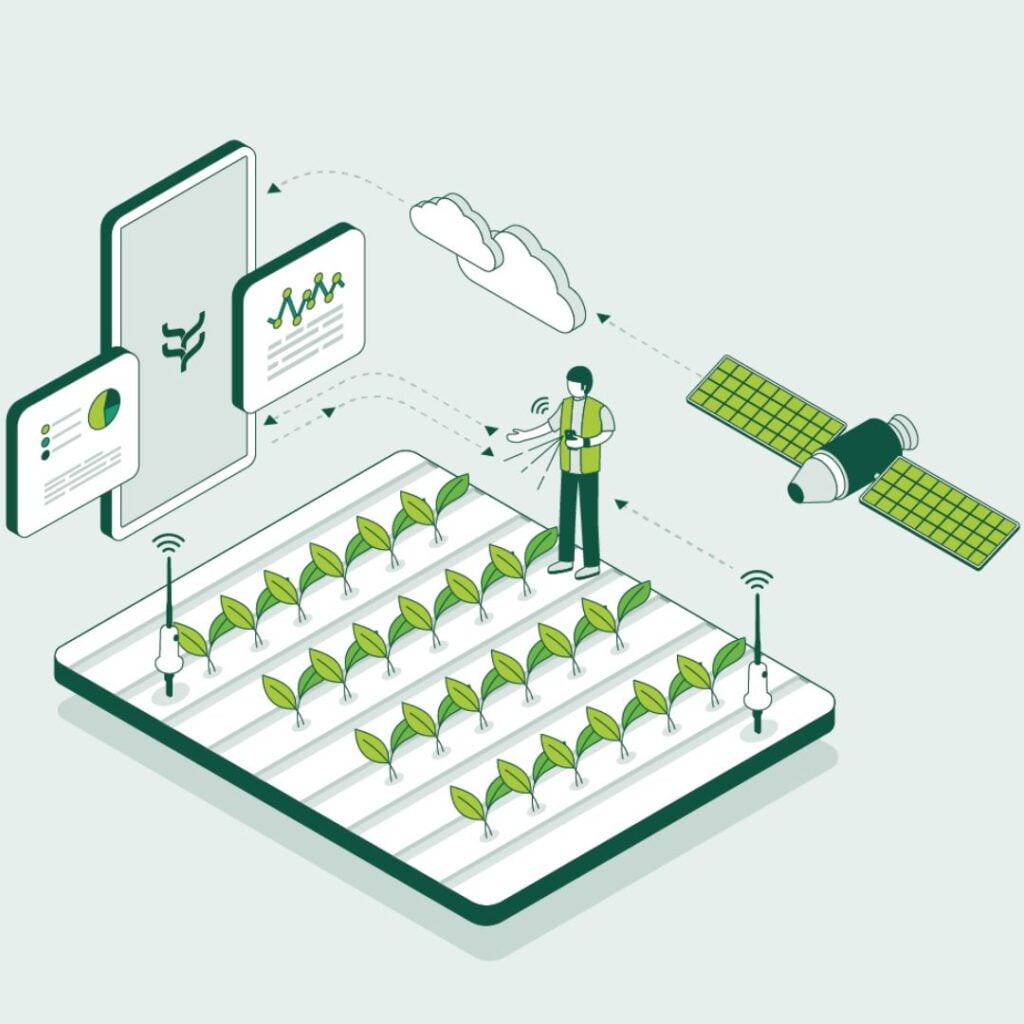

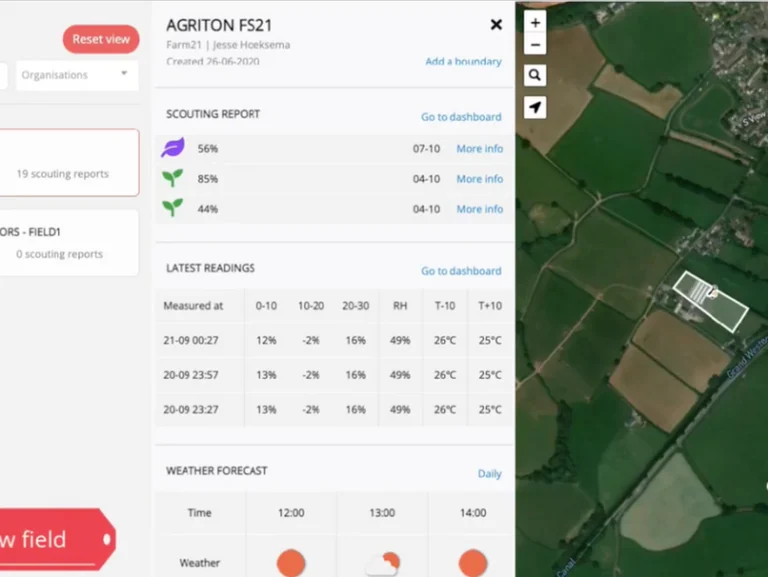
Farm21’s smart farming solution to support regenerative agriculture
At Farm21, we are dedicated to equipping farmers, crop advisors and researchers with the necessary knowledge and tools to support regenerative farming practices. We are committed to continually improving our innovative solution to assist farmers in managing their land and crops in the most efficient way possible.
The FS21
One of the key tools in our smart farming system is the affordable, easy to install soil moisture sensors. Our proprietary devices allow growers to monitor soil moisture and temperature at different depths, as well as air temperature and air humidity below the crop canopy. The data forms the foundation on which users can base decisions about irrigation, fertilisation, and other management practices. This, in turn, can help to reduce waste, improve crop yields, and promote healthy soil that supports biodiversity.
| Key Advantages | Farm21 | Competitors |
| Data collected from our proprietary low-cost sensors, scouting, satellite, weather, fields | ✅ | Single datasource |
| Configure your own alerts | ✅ | ❎ |
| Web and mobile app | ✅ | Need to install another app |
| Unlimited users for free | ✅ | Not possible to share data or pay extra |
| Free scouting app and satellite imagery | ✅ | ❎ |
| Easy to use interface | ✅ | ❎ |
| Phone, mail and chat support included | ✅ | Pay extra |
| API to integrate with your own platform | ✅ | Hardware focused |
Premium satellite data
In addition to soil sensors, Farm21 also uses data from remote sensing technologies to monitor crop growth and identify areas of stress. This allows farmers to make more informed decisions about crop management, reducing the need for chemical inputs and promoting healthy soil that supports biodiversity.
Farm21 data platform and app
Bringing it all together in one central hub, Farm21’s data platform allow users to collect, store, access analyse data from multiple sources, including soil sensors, satellites, and weather applications. The data can be transformed into valuable insights so that farmers can make more informed decisions when implementing regenerative agriculture practices.
Schedule a meeting with one of our global partnership managers
Conclusion
In conclusion, regenerative agriculture is a holistic approach to farming that not only sustains the land but also regenerates it, leaving it more productive and resilient for future generations. By embracing precision ag tools, growers can adopt regenerative practices, leading to overall balance and long-term sustainability. Soil moisture sensors, remote sensing, and farming data platforms are just a few of the many tools and technologies available to support regenerative agriculture practices.
It is imperative that we continue to explore new ways of utilising technology to promote sustainable agricultural systems. As we move forward, it is essential that we prioritise regenerative practices that support the health of our planet, rather than deplete it. By working with nature, not against it, we can promote regenerative agriculture and ensure that we leave a better world for future generations.