The True Value of Better Farming Insights: How to Set Yourself Up for Success

Gaining better farming insights is the key to unlocking the full potential of modern agriculture. By acquiring comprehensive knowledge and utilising precision farming tools and techniques, farmers can optimise productivity, enhance resource management, and ensure long-term sustainability. In this article, we will explore the true value of better farming insights and provide practical guidelines on how to set yourself up for success.

Better Farming Insights: What Does It Really Mean?
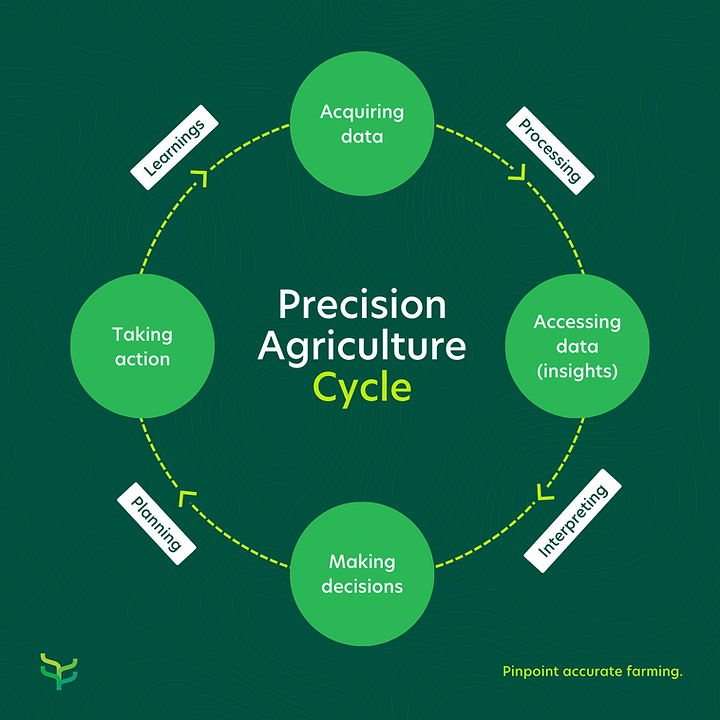
Better farming insights refer to the comprehensive understanding and knowledge gained through data collection, analysis, and interpretation in the agricultural context. It involves utilising various tools, technologies, and techniques to gather information about soil health, weather patterns, crop performance, resource usage, and other relevant factors. These insights provide growers, researchers and crop advisors with a deeper understanding of what is happening in their fields, enabling them to make informed decisions and take proactive actions to optimise productivity, enhance resource management, and ensure long-term sustainability.
By acquiring these insights, agri professionals gain a clearer picture of the current state of their farm and the factors that influence crop growth and overall agricultural outcomes. It involves analysing data from different sources such as remote sensing, sensor technology, weather monitoring, and historical records. This, in turn, helps to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that can guide them in making strategic decisions regarding irrigation scheduling, nutrient application, pest management, crop rotation, and other essential aspects of farming.
Moreover, better farming insights contribute to continuous improvement and learning within the agricultural sector. Growers can monitor the outcomes of their decisions and measure the effectiveness of different management practices. By tracking data over time, they can assess the impact of their actions, identify areas for improvement, and adapt their strategies accordingly. This iterative process enables farmers to fine-tune their operations and optimise performance, ultimately leading to increased productivity, profitability, and sustainability. (Read more about the concept of balanced farming in our previous blog post)

Rising to the Challenges With More and Improved Insights

Changing Climate Patterns

Population Growth

Consumer Preferences
Changing Climate Patterns
In today’s ever-evolving agricultural industry, there is an undeniable need for better farming insights. This need arises from the challenges that farmers face in their pursuit of productivity, sustainability, and profitability. One of the primary challenges is the changing climate patterns that impact crop growth and harvests. Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events pose significant risks to agricultural production. By gaining better farming insights, farmers can better understand these climate patterns, anticipate potential risks, and implement strategies to mitigate their impact.
Population Growth
Perhaps the biggest and most pressing challenge is the rapid growth of the global population, which puts immense pressure on the agricultural sector to produce more food (an estimated 60% more by 2050 to feed a world population of 9.3 billion). The need for increased food production must be balanced with the limited availability of resources such as land, water, and energy. Better farming insights enable farmers to optimize resource management by accurately assessing crop water requirements, determining precise nutrient applications, and adopting efficient irrigation practices. By making informed decisions based on data-driven insights, farmers can maximise resource utilisation, minimise waste, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices.
Market Dynamics and Consumer Preferences
Furthermore, market dynamics and consumer preferences play a role in the need for better farming insights. Consumers are becoming increasingly conscious about the origin and production methods of their food. They demand transparency, traceability, and sustainability in their food choices. To meet these demands, farmers must have a deep understanding of their production processes and be able to provide data-backed evidence of sustainable practices. Better farming insights enable farmers to monitor and track their farming practices, demonstrate compliance with sustainability standards, and build trust with consumers.

Key Strategies for Gaining Better Insights
Growers, researchers, and crop advisors can gain better farming insights through various approaches and methodologies. Here are some key strategies that can help them:
Data Collection and Monitoring
- Implementing remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and drone surveys, to capture detailed field data on crop health, biomass, and growth patterns.
- Utilising sensor technologies, like soil moisture sensors and weather stations, to collect real-time data on soil conditions, weather parameters, and environmental factors.
- Conducting regular field observations and inspections to gather qualitative information on crop performance, pest and disease incidence, and other on-ground observations.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Utilising data analytics and visualisation tools to analyse large datasets, identify patterns, and extract meaningful insights.
- Applying statistical methods and modelling techniques to correlate different factors and understand the relationships between variables.
- Engaging in data-driven research and experimentation to evaluate the effectiveness of different agricultural practices and interventions.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
- Participating in research networks, agricultural forums, and conferences to exchange knowledge, share experiences, and learn from peers and experts.
- Collaborating with other growers, researchers, and advisors to conduct joint studies, field trials, and demonstrations that generate valuable insights.
- Leveraging online platforms and digital communities to access information, research findings, and best practices shared by industry professionals.
Adoption of Precision Farming Tools and Techniques
- Implementing precision agriculture technologies, such as GPS-guided machinery, variable rate application systems, and automated irrigation systems, to optimise resource usage and improve farming efficiency.
- Utilising geographic information systems (GIS) and mapping tools to assess field variability, delineate management zones, and customise farming practices based on spatial data.
- Embracing digital farm management platforms that integrate data from multiple sources, provide analytics and decision support tools, and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
- Staying updated with the latest advancements in agricultural technology, research findings, and industry trends through continuous learning initiatives, workshops, and training programs.
- Engaging in professional associations, certification programs, and educational courses that focus on precision agriculture, agronomy, and farm management.
- Seeking guidance from experienced crop advisors and consultants who possess domain expertise and can provide tailored recommendations based on specific farming contexts.
By embracing these approaches, growers, researchers, and crop advisors can enhance their understanding of agricultural systems, gain valuable insights into crop performance, optimise resource management, and make informed decisions to improve farming practices. The combination of data-driven approaches, collaboration, and continuous learning is instrumental in achieving better farming insights and driving positive change within the agricultural sector.

Small Precision Farming Tools That Make a Big Difference
Precision farming tools play a crucial role in helping growers, researchers, and crop advisors gain better farming insights by providing accurate and detailed data, enabling informed decision-making, and optimising agricultural practices. Let’s look at three affordable and simple precision farming tools that help you gather and analyse information and translate it into valuable insights.
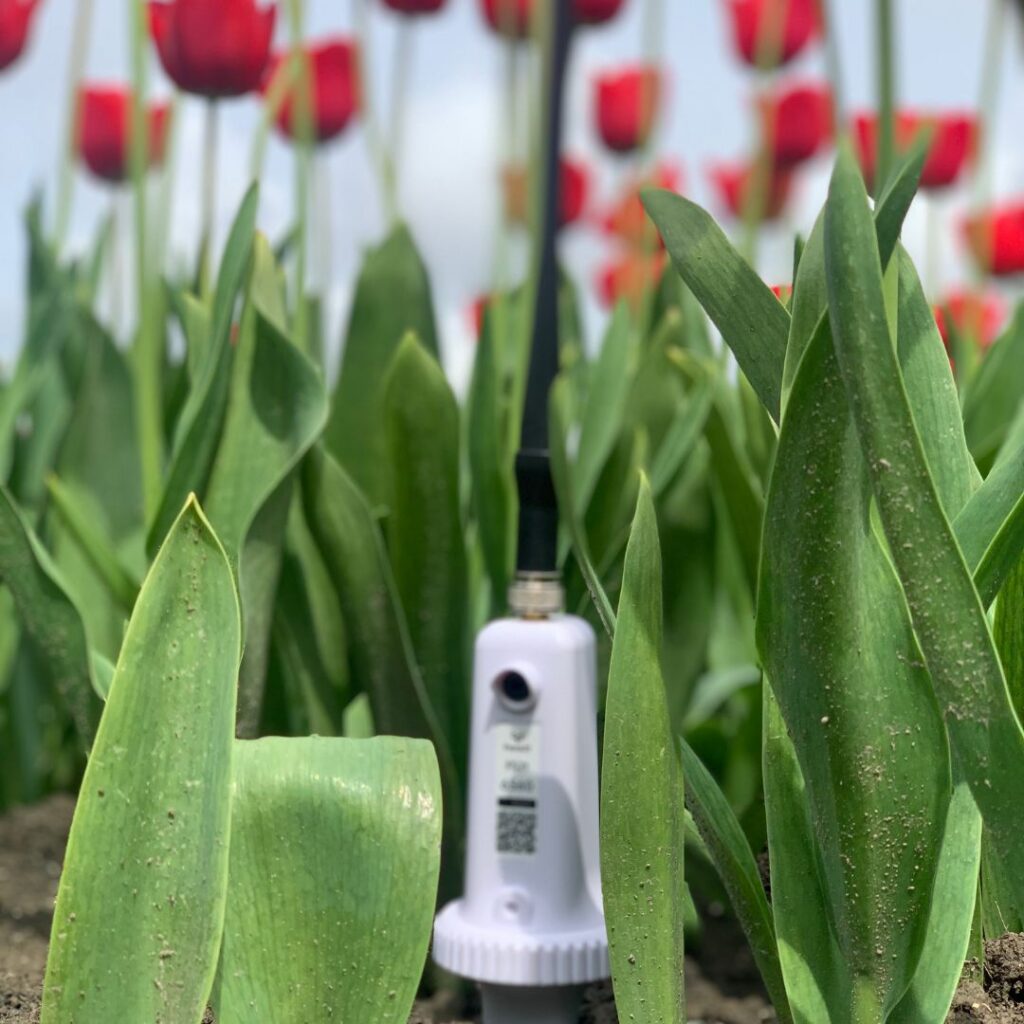

Soil Moisture Sensors

Remote Sensing Technology

Farming Data Platforms
Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors play a crucial role in gaining better farming insights by providing accurate and real-time data on soil moisture content. Here are some key ways in which soil moisture sensors contribute to this objective:
- Optimal Irrigation Management: Soil moisture sensors provide growers with precise information about the moisture levels in the soil, allowing for more efficient irrigation management. By monitoring soil moisture content at different depths, farmers can determine when and how much water should be applied to the crops. This data-driven approach ensures that irrigation is performed only when necessary, avoiding overwatering or under-watering. By optimising irrigation practices, farmers can conserve water resources, reduce water waste, and promote healthier plant growth.
- Understanding Field Variability: Soil moisture sensors provide insights into the variability of soil moisture across different areas of the field. By mapping and analysing the data collected from sensors, growers can identify areas with high or low moisture levels, which may indicate variations in soil texture, drainage, or other factors. This understanding of field variability allows for site-specific management practices, such as variable rate irrigation or targeted soil amendments, tailored to address specific soil moisture conditions in different zones. By addressing field variability, growers can optimise resource allocation and maximise the overall productivity of the farm.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Soil moisture sensors generate data that can be integrated with other agricultural data sources, such as weather information, crop growth models, and historical records. By combining this data, growers can make data-driven decisions related to irrigation scheduling, crop selection, and resource management. Analysing long-term soil moisture data trends can also provide valuable insights into soil health, drainage patterns, and the effectiveness of irrigation practices over time. This information helps growers refine their farming strategies, adapt to changing conditions, and optimise their operations for improved outcomes.
Remote Sensing Technology
Satellite data can be an extremely valuable way to gain better farming insights by providing valuable information about various agricultural parameters and conditions. Here are some ways in which satellite data can contribute to this objective:
- Detection of Crop Stress and Disease Outbreaks: Satellite data can aid in the early detection of crop stress, diseases, and pest infestations. By analysing satellite imagery, growers can identify anomalies in crop health, such as areas with reduced vegetation vigour or unusual patterns. This early warning system enables farmers to take timely action, implementing targeted interventions to mitigate crop losses. By detecting stress factors and disease outbreaks at an early stage, satellite data contributes to improved pest management, disease control, and overall crop health.
- Land Cover and Land Use Mapping: Satellite data enables the mapping and monitoring of land cover and land use patterns. This information helps in identifying different types of crops, tracking changes in land use, and assessing the extent of agricultural activities. By understanding the distribution and dynamics of land cover, growers and researchers can make informed decisions regarding crop rotation, land management, and conservation practices. Satellite-derived land cover mapping also facilitates the assessment of ecosystem services, such as habitat conservation and biodiversity preservation.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Satellite data facilitates the assessment of environmental impacts associated with agricultural practices. By monitoring land use changes, water resources, and soil degradation, satellites contribute to evaluating the sustainability of farming activities. This information helps policymakers, researchers, and growers identify areas of concern, develop conservation strategies, and implement measures to minimise environmental impacts.
Farming Data Platforms
Agriculture data platforms and apps play a pivotal role in gaining better farming insights by centralizing, analyzing, and visualizing agricultural data in a user-friendly and accessible manner. Here are some ways in which agriculture data platforms and apps can contribute to this objective:
- Data Integration and Organization: Agriculture data platforms enable growers, researchers, and crop advisors to integrate diverse data sources into a centralized system. These platforms can collect and store data from various sensors, weather stations, satellite imagery, and on-ground observations. By organizing data in a structured manner, agriculture data platforms provide a comprehensive view of the farm, facilitating data analysis and interpretation.
- Real-time Monitoring and Decision Support: Agriculture apps and platforms offer real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing farmers to track critical parameters such as soil moisture, weather conditions, crop growth, and pest outbreaks. By receiving timely alerts and notifications, growers can make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, disease management, and other farm activities. Decision support tools within these platforms provide recommendations based on data analysis and predictive modeling, assisting farmers in optimizing their practices for better outcomes.
- Historical Data Analysis and Trend Identification: Agriculture data platforms enable the analysis of historical data, allowing growers to identify trends, patterns, and correlations. By analyzing data over multiple seasons or years, farmers can gain insights into long-term trends, such as crop productivity, soil fertility, or climate impacts. This historical analysis helps in making informed decisions, such as selecting appropriate crop varieties, adjusting planting dates, or implementing soil management practices.
- Data Visualization and Reporting: Agriculture apps and platforms provide intuitive data visualization tools that transform complex data sets into easy-to-understand charts, graphs, and maps. These visual representations help growers and advisors gain insights at a glance, identify spatial patterns, and communicate findings effectively. Reports and dashboards generated by these platforms summarize key metrics and trends, enabling stakeholders to track performance, monitor progress, and share information with others.
- Collaborative and Knowledge Sharing: Agriculture data platforms often incorporate collaboration features, allowing growers, researchers, and advisors to share data, insights, and best practices. These platforms foster knowledge exchange and collaboration within the agricultural community, enabling users to learn from each other’s experiences, discuss challenges, and collectively work towards improving farming practices. By leveraging collective wisdom and shared data, users can gain new perspectives, access expert advice, and enhance their decision-making capabilities.
- Integration with Precision Farming Tools: Agriculture data platforms can integrate with precision farming tools, such as soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and yield monitors, to streamline data collection and analysis. This integration enables seamless data transfer, eliminating manual data entry and ensuring data accuracy. By combining data from different sources, growers can gain a holistic view of their operations, analyze relationships between variables, and make data-driven decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of their farm.

Farm21’s Smart Farming Solution to Gain Better Insights
At Farm21, we are dedicated to equipping farmers, crop advisors and researchers with the necessary knowledge and tools to collect and analyse as much information as possible and turn it into valuable insights. Out team of hardware and software developers, data analysts and precision farming experts are committed to creating affordable, easy-to-use smart farming tools:
The FS21
Our proprietary, second generation soil moisture sensors provide the 7 most critical values necessary for data-driven decision. Measuring soil moisture and temperature at different depths, as well as air temperature and air humidity below the crop canopy, the data provides valuable insights on which users can base decisions about irrigation, fertilisation, and other management practices.
Premium Satellite Data
In addition to soil sensors, premium satellite offering provides valuable insights into crop growth and allow users to quickly identify areas of stress and take proactive action. This, in turn, leads to more more informed decisions about crop management and optimised resource usage.
Farm21 data platform and app
Bringing it all together in one central hub, Farm21’s data platform allow users to collect, store, access analyse data from multiple sources, including soil sensors, satellites, and weather applications. The data can be transformed into valuable insights so that users can base their decisions on facts.
Schedule a meeting with one of our global partnership managers:
Conclusion
Ultimately, gaining better farming insights is crucial for farmers to navigate the complex and ever-changing agricultural landscape. By harnessing the power of data and adopting precision farming tools and techniques, farmers can make informed decisions that lead to improved productivity, enhanced resource management, and long-term sustainability.
The ability to understand and interpret data allows farmers to identify opportunities, optimise farming practices, mitigate risks, and adapt to changing circumstances. In a world where every decision counts, better farming insights provide a competitive edge and pave the way for a prosperous and sustainable future for farmers and the agricultural industry as a whole.